The fast evolution of modern digital technologies made the IT services market incredibly competitive, pushing companies operating on it to adopt agile development. To facilitate this approach, agile Scrum model comes as one of the most effective options. This specialized framework allows for ensuring timely delivery of quality and innovative products across the software product lifecycle.
To successfully manage complex projects, one should have a thorough understanding of the Scrum model. This article sheds light on the basics of Scrum alongside a quick review of the scrum methodology phases.
Let’s start exploring.
What Is Scrum Methodology
When talking about agile software development, people usually consider Scrum as a methodology. However, at the end of the day, Scrum is not a methodology, rather a practical method.
More specifically, Scrum is a framework that allows for heuristic implementation of agile development while also replacing the algorithmic approach. It is an iterative process that allows you to develop software in phases and get solid final product.

Scrum Framework
Most software development teams prefer using agile methodology Scrum for their projects. Some developers also use a Scrum hybrid, which means combining Scrum with Kanban and Lean practices.
While the IT industry is the one who leverages it the mostg, agile Scrum methodology is being adopted by other niches as well. For example, companies in the advertising industry also use this approach for complex projects that require flexibility to stay efficient . As a result, Scrum has emerged as a standalone project management approach beyond IT.
Principles Of Scrum Methodology
Scrum principles drive the entire framework. An organization can conveniently adopt the scrum model for project management by simply adhering to these principles. They can be slightly modified to fit project requirements, but only slightly. Otherwise, there is a risk that your efforts in implementing the Scrum framework will not yield the result you expected to have.
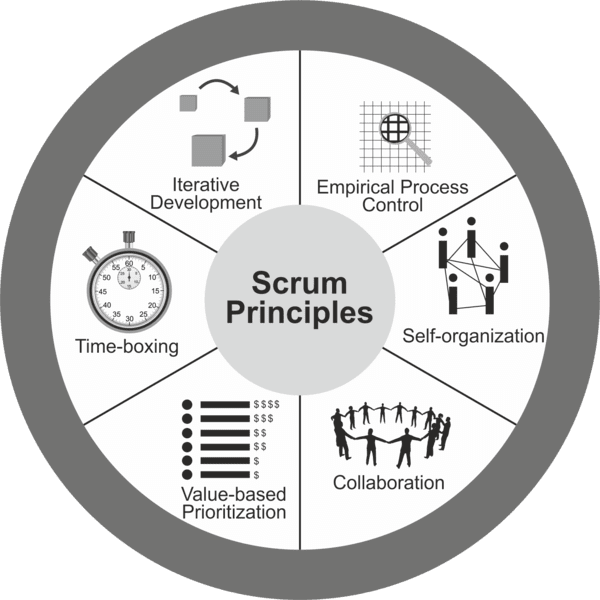
Principles of Scrum
- Empirical Process Control. It is critical to implement the three core ideas of the Scrum philosophy – transparency, inspection, and adaptation. This can only be achieved with consistent process control.
- Self-organization. While Scrum supports teamwork, it also focuses on empowering each individual on the team. Thus, self-organization is another basic principle of the Scrum agile methodology.
- Collaboration. Collaboration is at the core of the Scrum model of agile development. Focusing on the key ideas of cognizance, articulation, and adoption, this principle provide a reliable foundation for project management and development process.
- Value-based Prioritization. Implementation of this principle in the beginning of the project allows you to gain one of the key benefits of Scrum – maximum project value.
- Time-boxing. Using this principle in all agile Scrum phases is what makes Scrum distinct from other software development approaches. Time-boxing allows teams to deliver the final result on time regardless of the complexity and project size.
- Iterative Development. One of the prime focuses of Scrum is client satisfaction. To help teams achieve that, Scrum incorporates phases. After a phase (which usually represents creating a part of the product) is over, the client leaves their feedback, the team makes all necessary changes, and then the everybody proceeds to the next stage of the Scrum model in SDLC.
Project Roles In Scrum Methodology Steps
The entire framework of Scrum model is driven at the level of teams. It does not focus solely on individuals, but individuals working together in a team to successfully deliver a solid final result.
Usually, a scrum team comprises of three main roles:
- Product Owner – ensures the end user is engaged in the product.
- Scrum Master – manages the proper implementation of Scrum process in the team and coordinates the entire process.
- Development Team – self-organizing and cross-functional units responsible for the execution of tasks and aiming at a solid final result.
Overview Of Events In Scrum Phases
Sprint
Sprint is the core of all steps in the Scrum methodology. It refers to the time-boxed period needed for the completion and review of a a certain part of the product.
Sprint Planning
Sprint planning meetings give teams an opportunity to manage the product backlog and delivery. Like all other steps of the agile Scrum model, Sprint Planning is also a time-boxed event.
Daily Scrum Meeting
Ensuring one of the key Scrum methodology advantages – efficient teamwork – a daily scrum meeting is another brief event that allows team members to communicate and discuss the work in progress.
Sprint Review
Sprint Review enables the team to give the work they did during the previous sprint to the Product Owner for review. The Product Owner then accepts or rejects the results based on the criteria set forth earlier.
Retrospective
Sprint Retrospective is the last event in Scrum methodology implementation. This event refers to a meeting where the team discusses their overall progress and performance.
Scrum Model Diagram
The following diagram provides a visual representation of the events making up the Scrum model in software development.
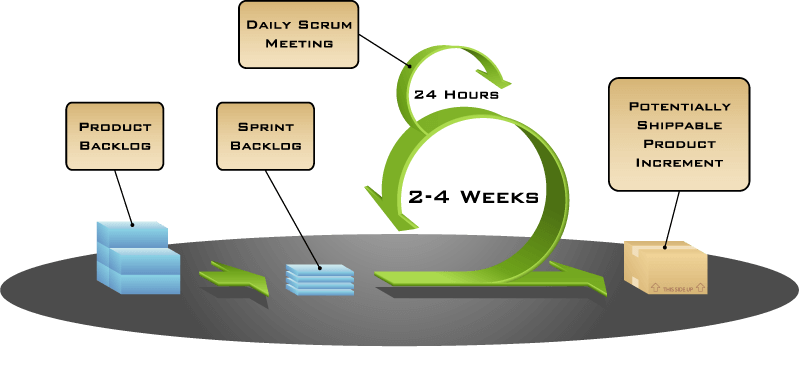
Agile Scrum Methodology Steps
The Scrum events described above do not just happen randomly during the development of a product. They happen step-by-step throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC) via the Scrum model.
Phase 1. Product Backlog
The development of software using the agile Scrum model begins with the creation of a product backlog. Here, the term backlog does not indicate any work that has been overdue. Instead, creating product backlog refers to the activity of listing out features to implement during the development phases. The list is made on a priority basis. Each item in the list is called a user story and marked with a unique ID. Then, a description of every user story is made that, which heavily assists in later stages. Each description includes important details, like why a particular user story is important, estimation of overall workload, and figuring out a plausible demonstration of the product. Besides these mandatory details, there are optional IDs like requestor and bug tracking.
Phase 2. How Many Days Is A Typical Sprint In The Scrum Methodology?
While the next major phase is Sprint Backlog creation, you can’t proceed to this step unless you determine Sprint Duration.
The usual duration for a Sprint is 2 to 4 weeks, or 15-30 days, with 30 days being the most common timeframe. However, in the end, it all depends on the situation. For example, designing and security engineering may entail longer sprint duration, with, a sprint extending to 6 or even 8 weeks.
In addition, sprint duration in a Scrum model also depends on your own and client’s preferences. With shorter sprints, you can frequently deliver the work to the client and gain continuous and quick feedback for the needed improvements and bug fixes. With longer sprints, you may choose to work thoroughly before showing a particular part of the product to the client.
Phase 3. Sprint Backlog & Planning
After you finished determining sprint duration, you need to tackle Sprint Backlog creation and planning. Based on the priority for a user story set up by the product owner, sprint backlog is created to determine what user stories would be covered during a sprint, keeping in view both the work required and the sprint duration. Once the sprint backlog is established, the team has to ensure timely completion of the work for all user stories.
Phase 4. Reviewing Sprint Progress & Conducting Meetings
The next important activity of the Scrum model in SDLC is effective communication of the work in progress. For this, a task board is maintained to depict the current status of all tasks handled by the team members. The team can simply use various sticky notes labeled with task numbers and/or details referring to a particular body of work. They can then move these sticky notes across the board to show the current status — ‘to do”, “in progress”, “testing” or ‘done”, etc.

Instead of using a conventional task board, Scrum teams can also use specialized software for this purpose, with Jira being among the most popular options..
In addition to the maintenance of the task board, other important activity is to ensure that daily Scrum meetings happen. In these meetings, the team members can discuss the work they completed, the work to be done, the problems teams members face in the process of tackling tasks, and the overall progress of development.
Phase 5. Reviewing, Testing & Demonstration of Product
Before delivering the working product to the client, the Scrum team thoroughly reviews the product by performing full life-cycle testing. More specifically, every Sprint is tested, demonstrated and reviewed to detect problems, bugs, or to see if there are any changes to make.
Phase 6. Sprint Retrospective & Planning For Next Sprint
In the final phase of the Scrum model software development life cycle, the team reviews the results obtained during a sprint and plans out the workability for the next one, as well as proposing potential improvements for future iterations.
Graphical Representation — Scrum Methodology Stages
This Scrum methodology diagram sums up the entire workflow of agile software development during various Scrum events.
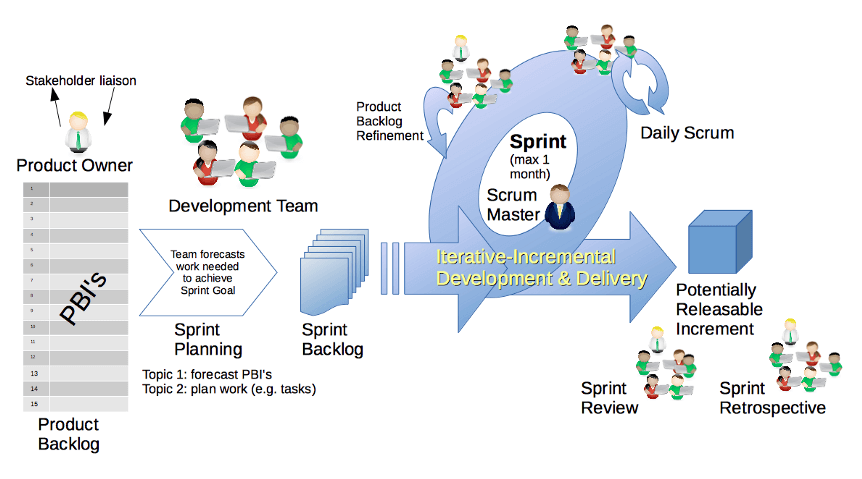
Scrum Model Advantages & Disadvantages
Scrum works best when you need to handle large complex projects that require streamlined teamwork. Nonetheless, like any other methodology, Scruma also has its downsides.
Let’s take a quick look at the Scrum methodology pros and cons.
Scrum Methodology Advantages:
- Increased productivity in complex and innovative projects
- Efficient utilization of time and resources
- Allows for faster completion of marketing projects
- Allows to build high-quality products
- High employee satisfaction
- High client satisfaction
Scrum Framework Disadvantages:
- Projects often lack focus and clarity at certain stages
- Requires skilled personnel/robust training
- May sometimes require organizational transformation
- Too many steps needed to scale large projects
- Daily meetings may be frustrating
Summing Up The Scrum Methodology
A robust problem-solving approach to modern projects, Scrum model of software development illustrates how effective and flexible the agile development approach is, and why it is widely popular today. In essence, it enhances the principles of agile to ensure higher quality, higher productivity, and higher client and employee satisfaction. The Scrum methodology is founded on productive communication between the company and the client’s stakeholders, paving the way for long-term partnerships.
Nonetheless, implementing the Scrum model is highly challenging. Thus, to gain maximum benefits from this framework, businesses and their Scrum master should ensure the team members work hard, communicate well, and maintain focus on assigned tasks continuously. They should be aware of the benefits of agile methodology Scrum as well as its downsides. Once the Scrum team and the stakeholders develop a rapport, the overall development process becomes easy, engaging, and effective, resulting in a high-quality final product delivered within the initially set time frame.